New Technologies & New Materials
Incorporating the technology and skills we have accumulated over the years through experience with external technology, SNYG is able to produce new technology and new materials.
1Understanding Customer’s Needs
2In-House Technical Examinations
3Development of New Material
4Productization
Examples of New Technologies and New Materials
Cladding Material
The Creation of SNW-850P (Patent #5632358)
Modifying Tribaloy T800, a material conventionally used on parts which are used in oil refining and petrochemical plants (800℃), we have developed a new material that holds higher hardness in extreme temperatures compared to T800.
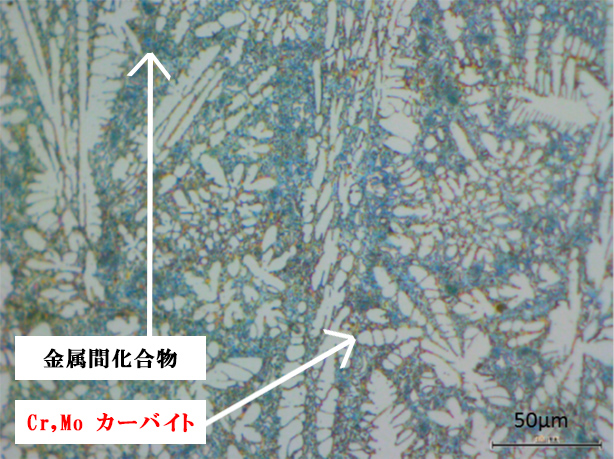
SNW850P
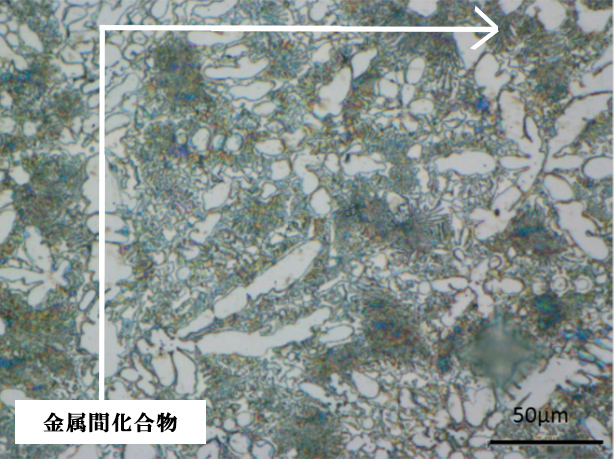
Tribaloy T800
Compared to Tribaloy T800, which is unstable in hardness throughout the surface due to the unbalanced intermetallic compounds, SNW-850P has not only a stable but also a higher hardness at high temperature by adding Cr and Mo.
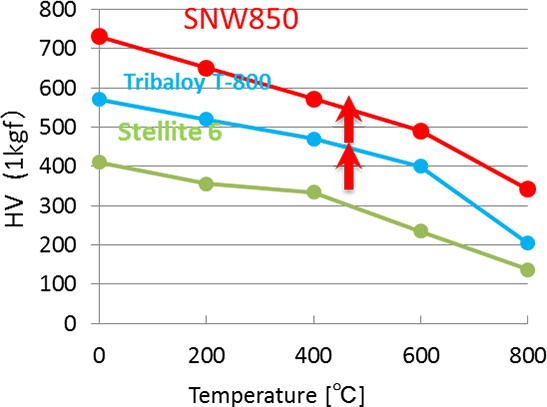
Hardness in High Temperatures
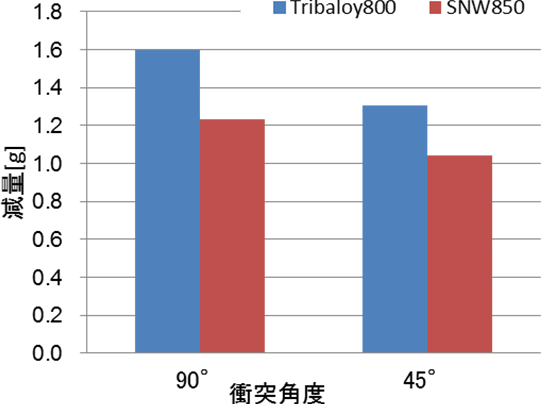
Jet Erosion Tests in Extreme Temperatures
Cladding Material 2
Laser Cladding
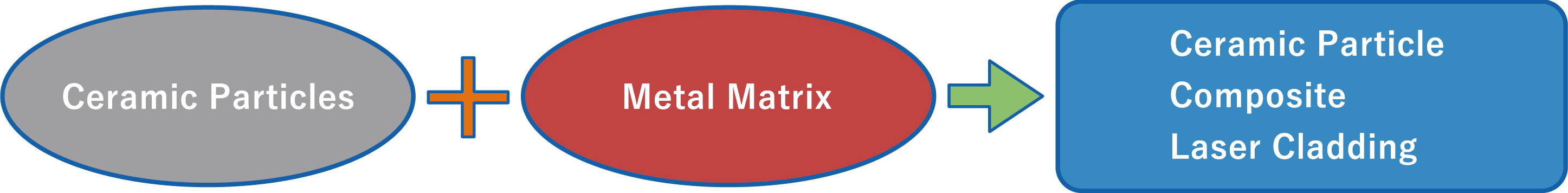
Ceramic Composite Laser Cladding
What is Ceramic Composite Laser Cladding?
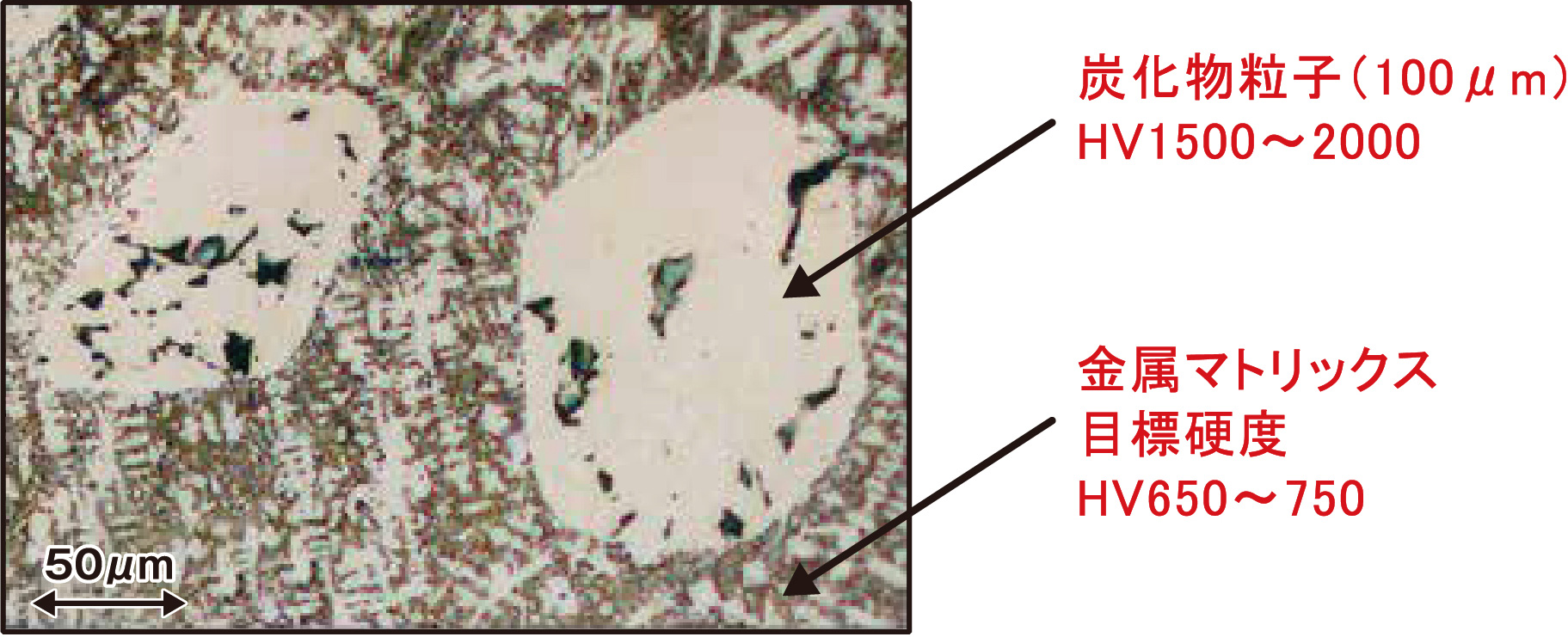
By using the Laser Cladding Technology, which clads at a much lower temperature than conventional systems, ceramic particles can be added without melting and maintaining its shape.
Characteristics
1. Ceramic Particle and Matrix Metal is selected according to the utility and purpose of the product
2. Being that the ceramic particles unmelt, cladded layer that holds the physical properties of both the ceramic particles and metal is produced
Test Results of Abrasion Resistance of Stellite© 6 + NbC Composite Laser Cladding
[Evaluation Method]
Suga Abrasion Test (AMPI)
[Evaluation Criteria]
Counterpart: SiC Paper #320
Number of Tests: 800
Weight: 3kg (abrasion ring width 6mm)
[Evaluated Material]
St.6+NbC Laser Cladding
St.6 Laser Cladding (for comparison)

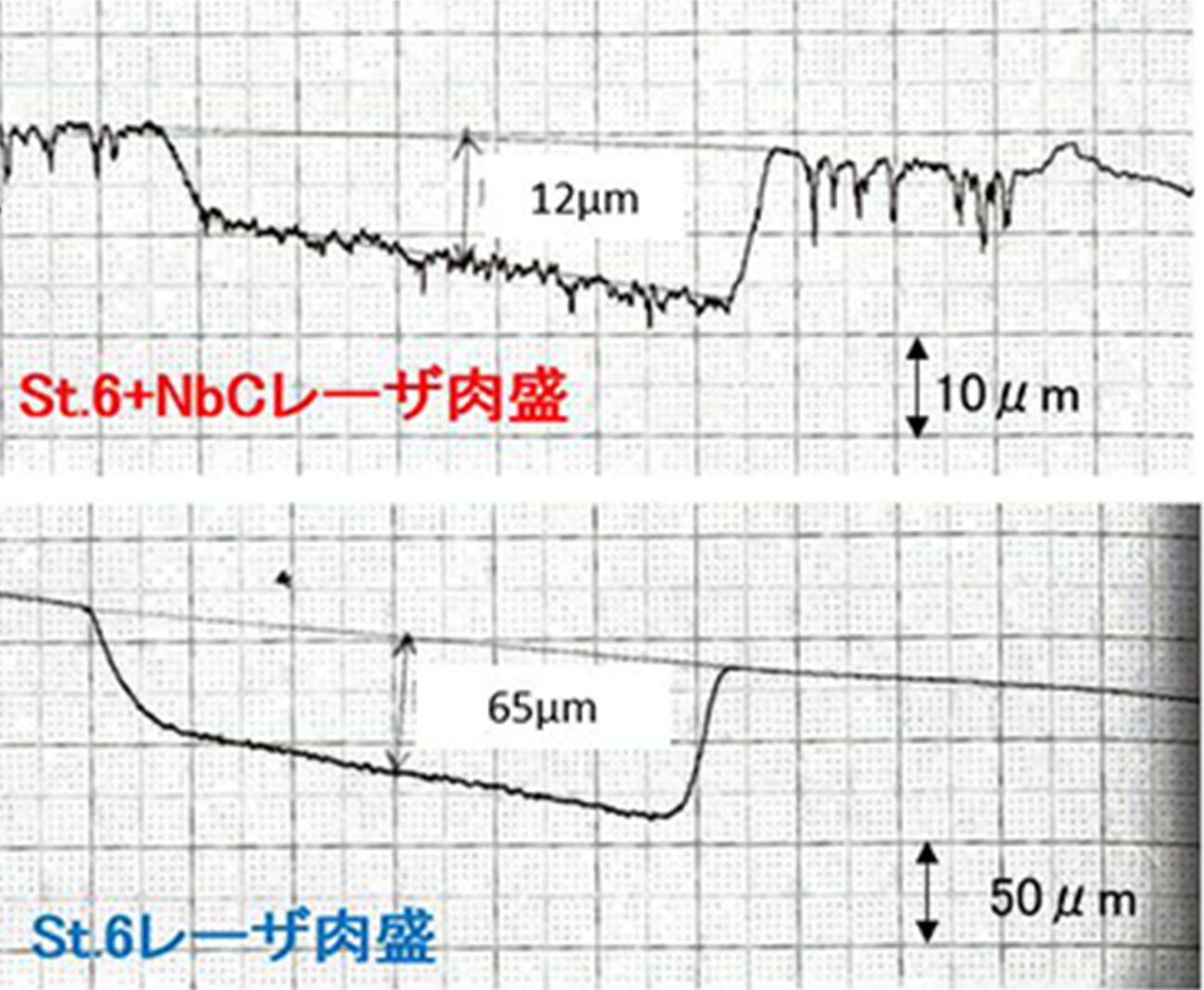
[Results of Measuring the Roughness of Abrasion Marks]
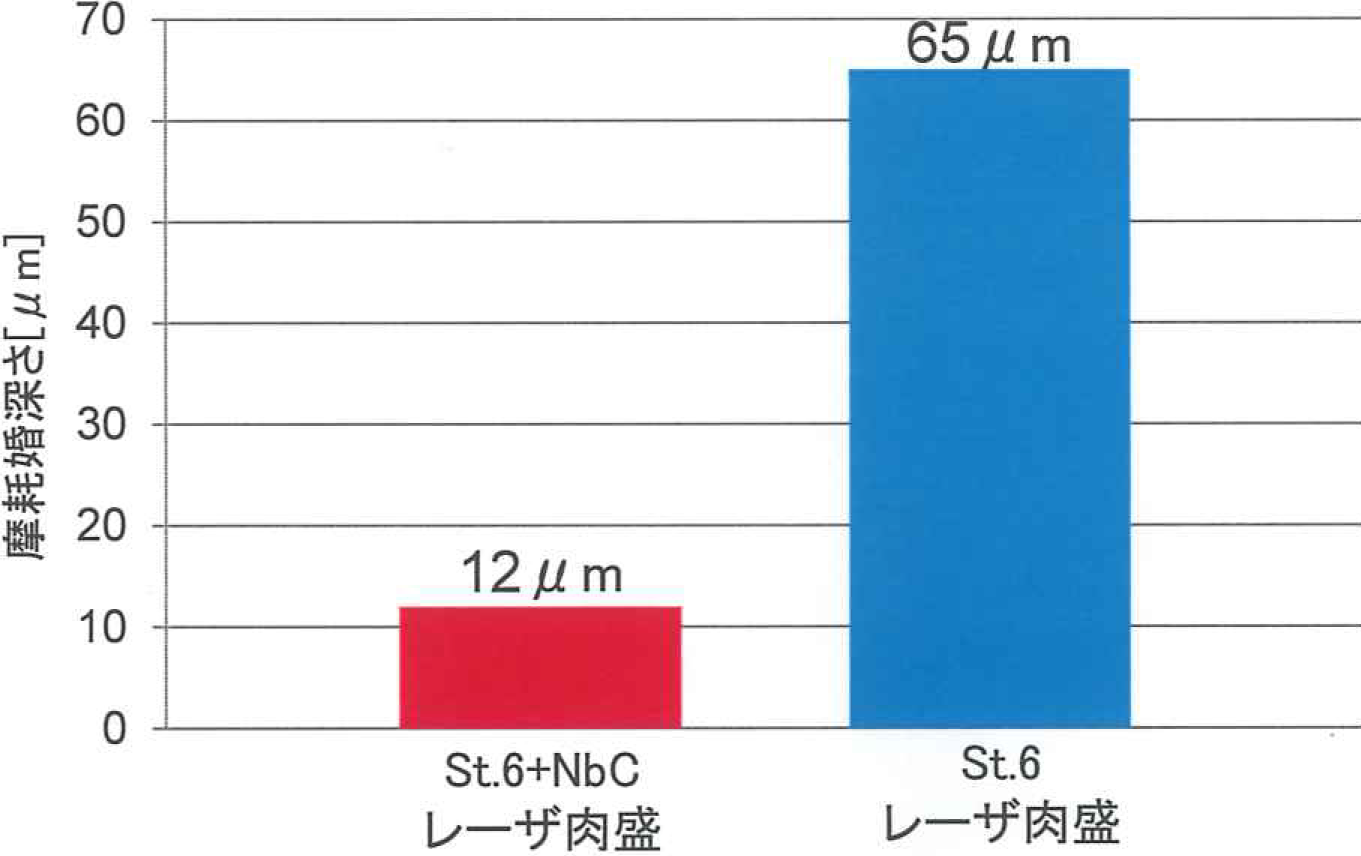
Shown to have Abrasion Resistance of 5 times higher in Lab test
Laser Cladding Surface Processing on Ductile Cast Iron
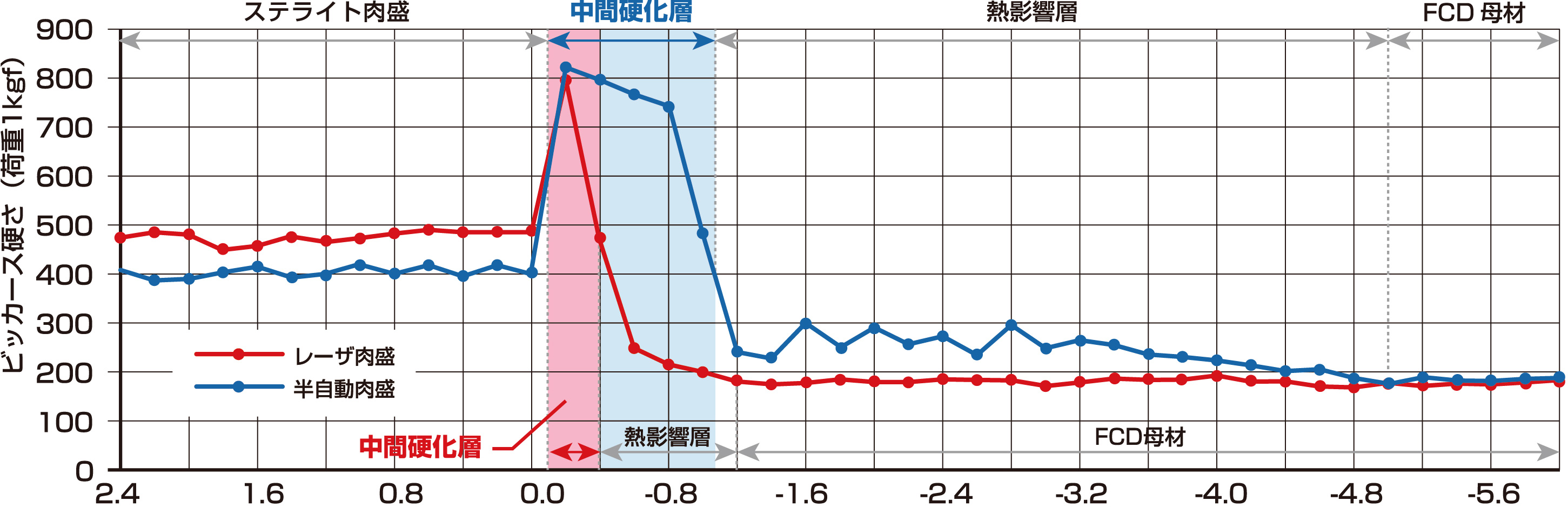
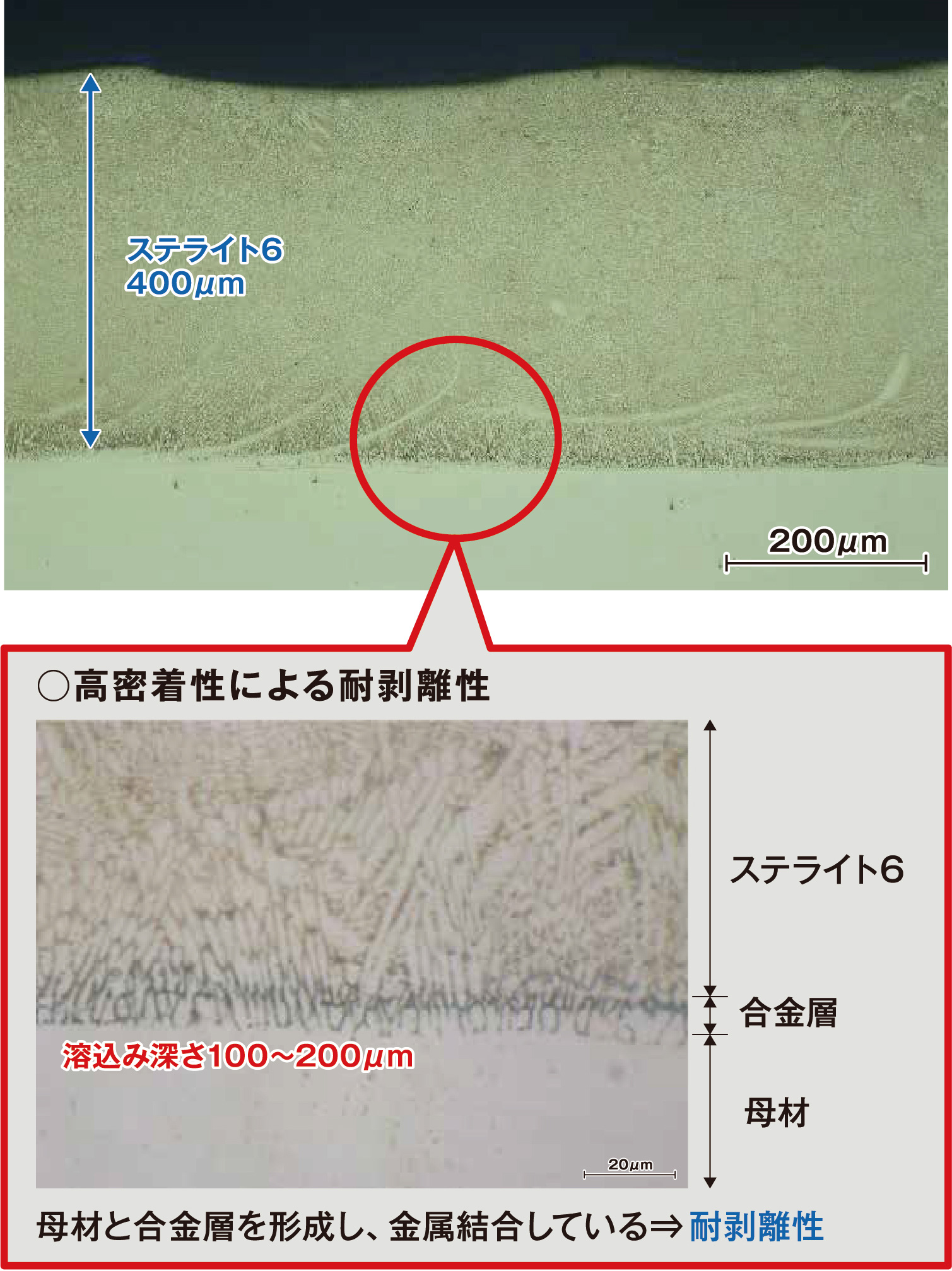
When cladding on Ductile Cast Iron, a diluted layer that is high-carbon and high-hardness is produced due to cladding dilution, making it prone to cracking and peeling.
Given this factor, we compared surfaces cladded using Semi-Automatic Overlay Welding and Laser Cladding; to suppresses the the quench-hardened layer.
Given this factor, we compared surfaces cladded using Semi-Automatic Overlay Welding and Laser Cladding; to suppresses the the quench-hardened layer.
| Cladding Material | Stellite© | |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | FCD450 | |
| Cladding Method | Laser Cladding | Semi-Automatic Overlay Welding |
| Magnified Cross Sectional view (Nital Etching) |
 |
 |
| SEM Image near Interface | 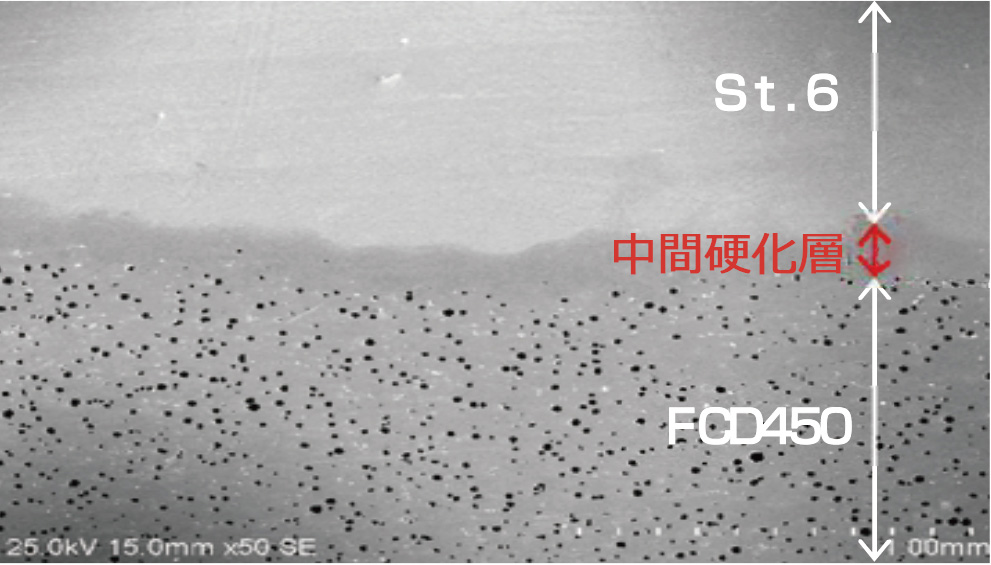 |
 |
| Cladding Height | 2.5mm | 2.5mm |
| Depth of Penetration | Under 0.5mm | 1.5mm |
| Depth of Intermediate Quench-Hardened Layer | 0.3mm | 0.9mm |
| Depth of Heat Affected Zone | Under 0.5mm | 4mm |
| Hardness of Stellite© #6 Cladded Layer HV450~500(HS 60~65) | HV450~500(HS 60~65) | HV380~420(HS 52~57) |
Distance from Cladding Boundary (mm)
When Cladding onto Ductile Cast Iron, we used Laser Cladding. With a lower dilution compared to Semi-Automatic Overlay Welding, Intermediate Quench-Hardened Layer and Heat Affect Zone are minimized, suppressing the risk of cracking and peeling. Furthermore, by obtaining a cladded layer with higher hardness, a higher degree of wear resistance is also promised.
エロージョン摩耗に対するレーザ肉盛開発材
高温で粒子が衝突する粉体エロージョンに対して、炭化物セラミックス粒子を未溶融で分散させる
セラミックスコンポジットレーザ肉盛を適用し、石油精製部品等の消耗品について長寿命化を図る。
セラミックスコンポジットレーザ肉盛を適用し、石油精製部品等の消耗品について長寿命化を図る。
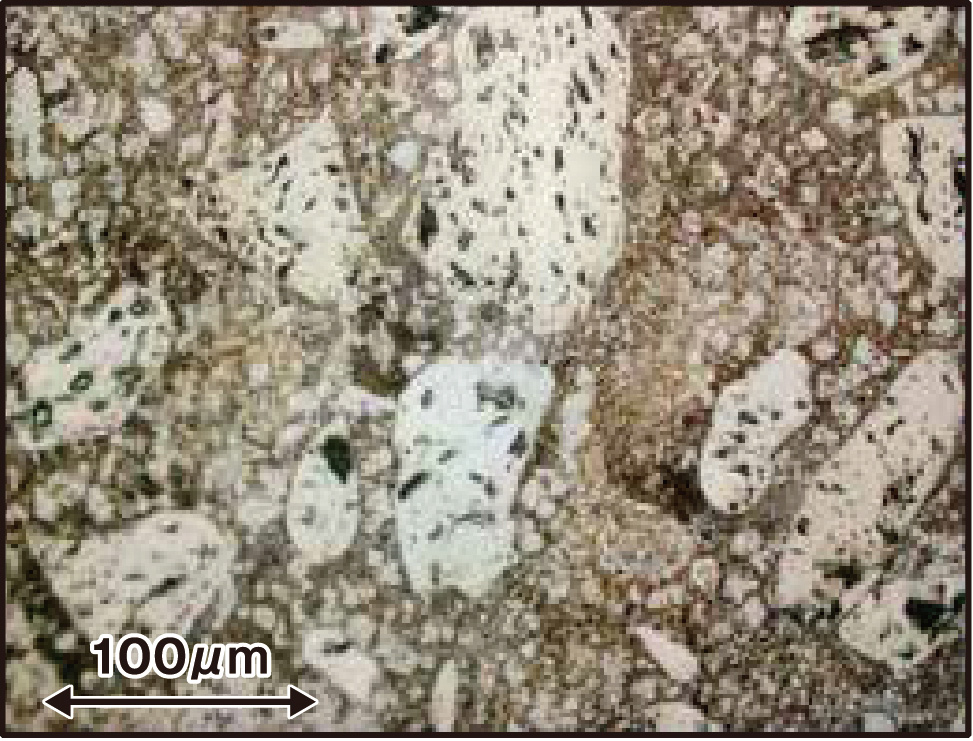
評価試験(組織観察)【含有炭化物量昇順】
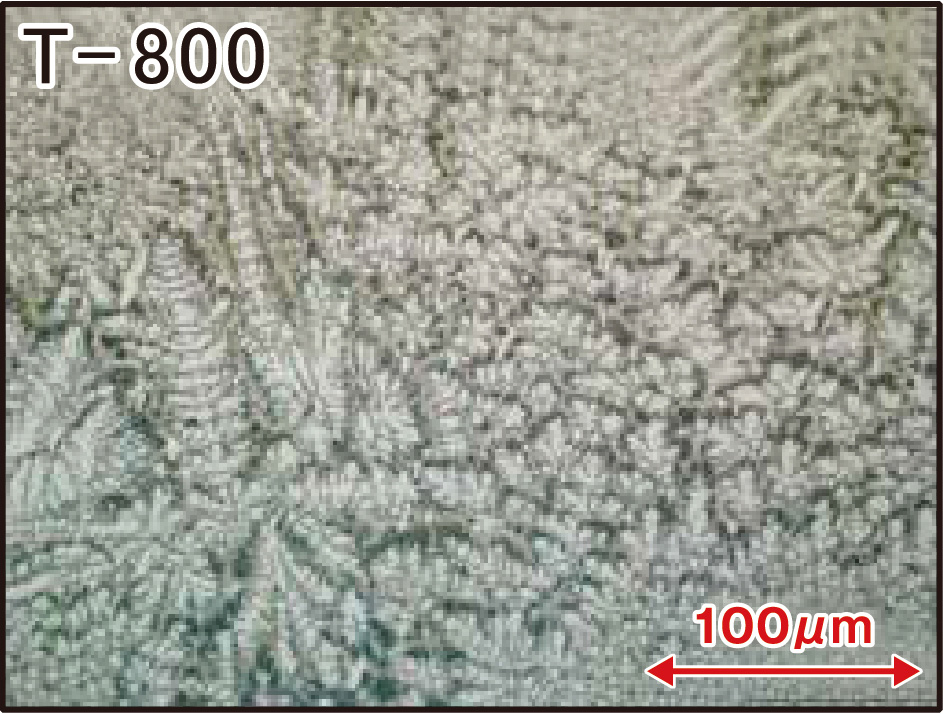

T-800
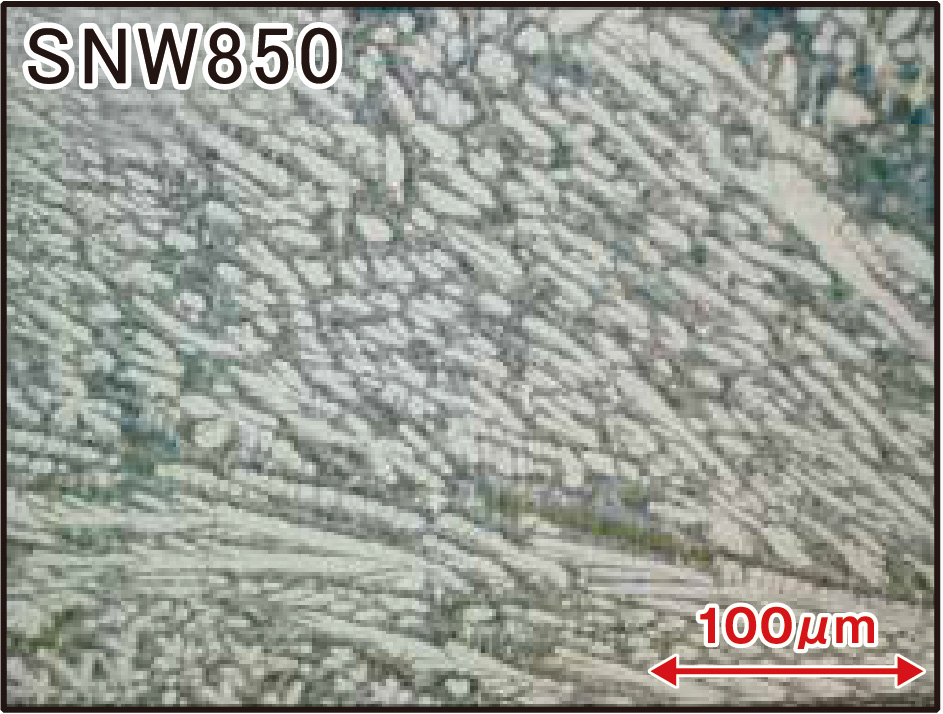

SNW850

開発材 SCL-S6C
Evaluation Test (Jet Erosion Test)
| Test Conditions | |
|---|---|
| Atmospheric Temperature | 500℃ |
| Particles | Alumni |
| Particle Size | 300~350μm |
| Collision Angle of Particles | 45°、90° |
| Particle Feed Rate | 200m/sec |
| Particle Feed Amount | 100g/min |
| Length of Test | 10min |
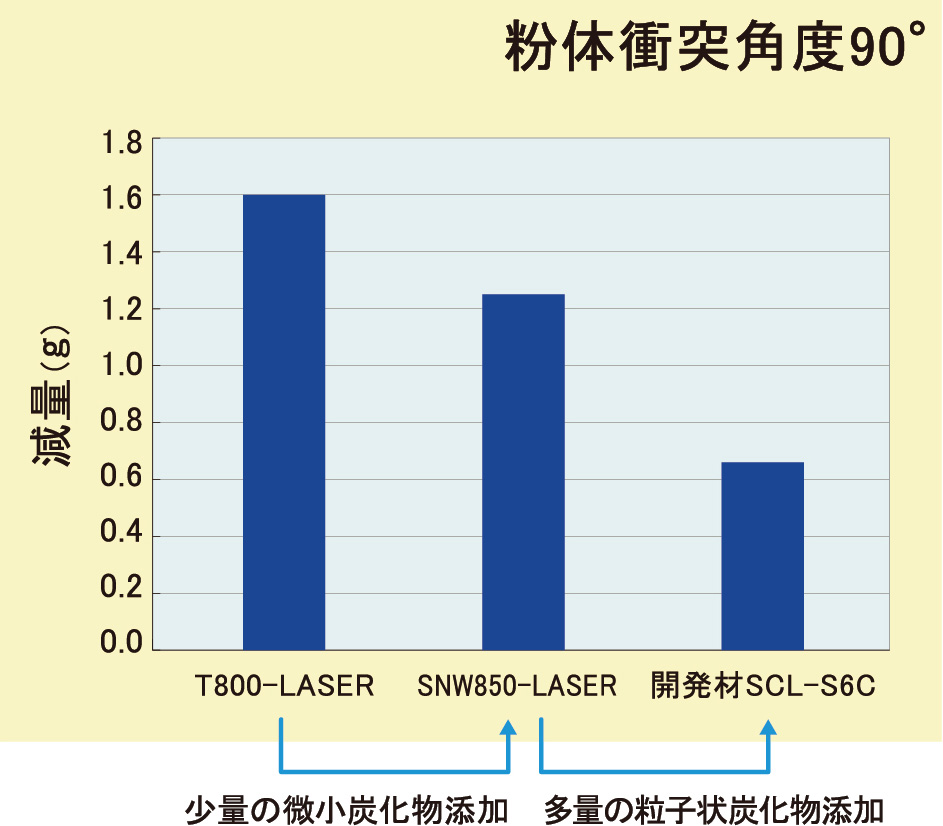
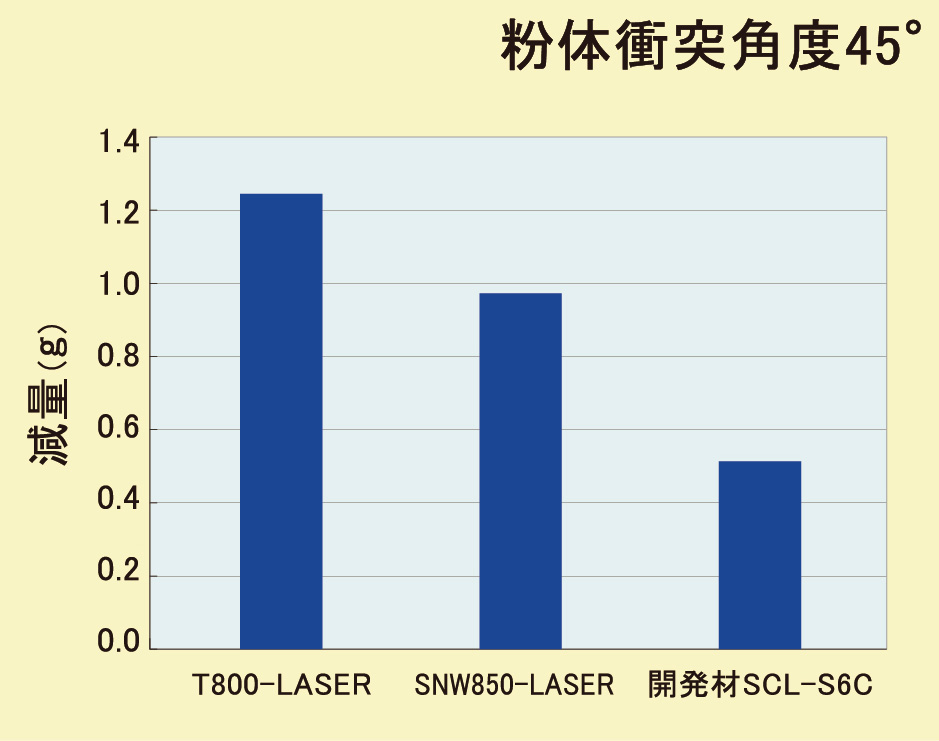
The Future of Erosion Resistant Cladding
To decrease the selected wear to the metal matrix caused by powder erosion, we will choose a matrix metal with a higher hardness to crease a material with a higher erosion resistance than SCL-S6C.

Thin Laser Cladding (Coating?)
Thin Laser Cladding produces layers with thickness of only a few hundred micrometers, but has higher resistance against peeling, wear, and corrosion, compared with other surface modification systems.
Stellite© #6 400μm
Thin Laser Cladding

High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Thermal Spraying
Corrosion Resistance that is Expected from the Internal Quality and Low Dilution
| Principal Component | Catalogue Value | Actual Value | Dilution Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cobalt | 55% | 50.8% | 7.6% |
| Chrome | 28.5% | 27.9% | 2.1% |
| Tungsten | 4.5% | 4.2% | 6.7% |
Low Porosity and Low Dilution ⇒Corrosion Resistance
The Corrosion Resistance Obtained Through Low Dilution and Fine Microstructure
High Hardness from Low Dilution and Fine Microstructure ⇒Corrosion Resistance
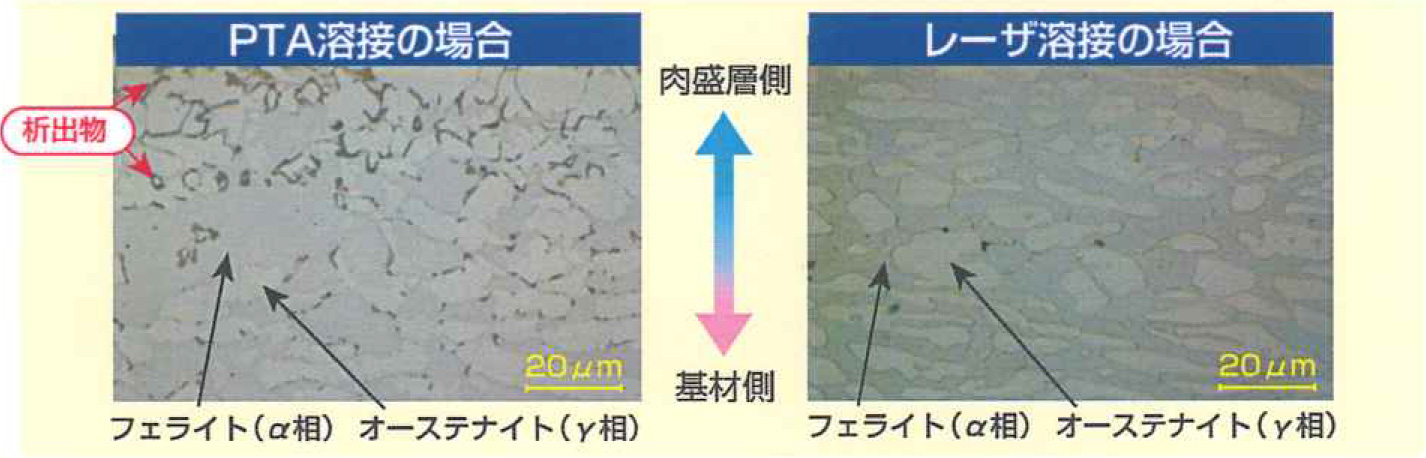
The Comparison between the Corrosion and Wear Resistance Property of PTA Cladding and Laser Cladding
The Property of the Heat Affect Zone of Stellite Cladded Duplex Stainless Steel
The issue with using Duplex Stainless Steel has been that Sigma Phase would deposit within the Heat Affected Zone, compromising the tenacity and the corrosion resistance. However, being that Laser Cladding has a much lower heat input compared to TIG and MIG/MAG Cladding, deposition within the Heat Affected Zone is reduced.
Microstructure of the Heat Affected Zone
Base Material: Duplex Stainless Steel SUS329J3L / Cladding Material: Stellite / Etching: Oxalic Acid Electrolytic Etching

The Features of SNW-850P
・Compositing carbide suppresses the unevenness of the hardness throughout the surface, generating higher overall hardness
・Compositing carbide miniaturizes microstructure
・Hardness is higher compared to conventional materials T-800 and Stellite #6 in high ~ room temperature
The Features of Laser Cladding
・Having lower Heat Input by Laser cladding methods than TIG and MIG/MAG, low dilution and ideal Physical Property of weld metal is obtained.
・Through having a lower heat input, base material (heat affected zone) maintains a higher quality
・Because it is quickly heated and quickly cooled, microstructure grains are finer
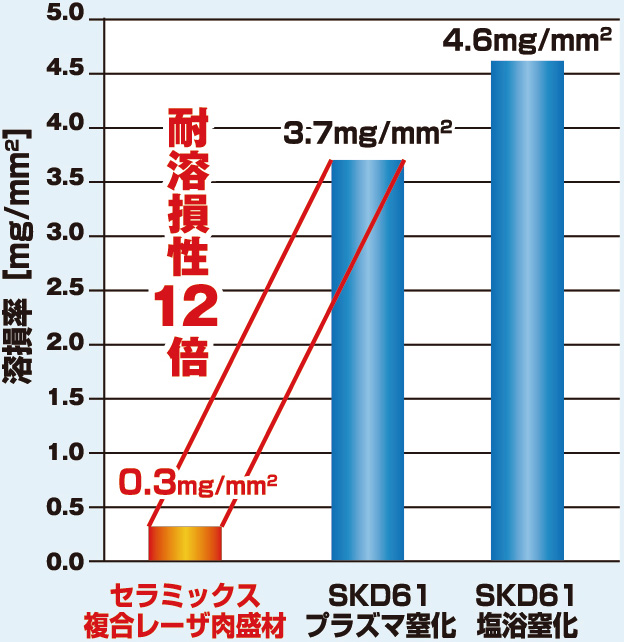
Evaluation of Ceramic Composite Laser Cladding Material’s Melting Resistance against Die-Casting Alloy (ADC12)
Cobalt Alloy based Laser Cladding material has highly abrasion and heat resistant ceramic carbide particles composite dispersed, making it have low reactiveness toward Molten Metal, showed promising results in tests against ADC12. It is highly anticipated that Ceramic Composite Laser Cladding’s resistance against dissolve loss to the metallic component will greatly contribute to the extension of consumable parts’ lifespan.
Comparison of Dissolve Loss against NItrided SKD61
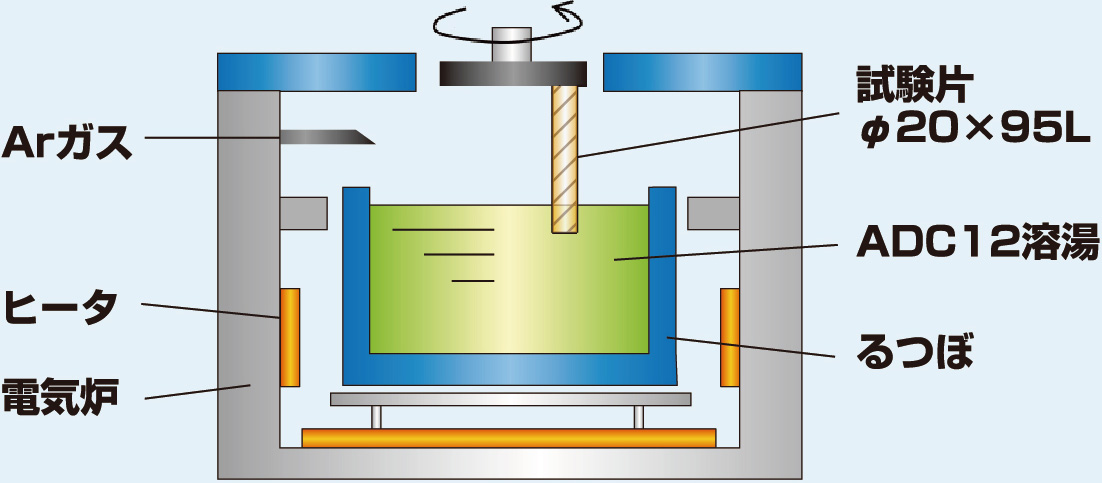
Schematic view of Testing Method
| Schematic view of Testing Method | ADC12(Al-Cu-Si) |
|---|---|
| Temperature of Molten Metal | 700℃ |
| Circumferential Velocity | 0.43m/sec |
| Testing Time | 5Hr |
| Tested Material | SKD61 |
Test Conditions
| Ceramic Composite Laser Cladding Material |
SKD61 with Plasma nitriding treatment |
SKD61 with Plasma salt bath nitriding treatment |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnified Cross Sectional View Before Tests |
 |
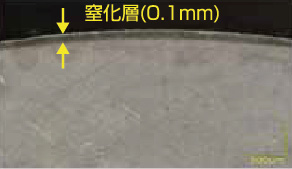 |
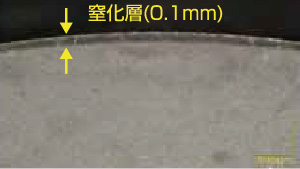 |
| External view after Test |
 |
 |
 |
| Cross Sectional View after Test |
 |
 |
 |
Test Results果
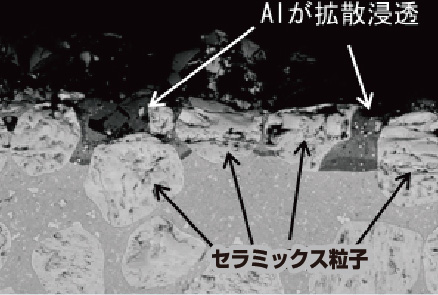
SEM Image of Ceramic Composite Laser Cladded Layer after Testing
After tests the cross-sectional observation of the Ceramic Composite Laser Cladding showed that the diffusion penetration of the Aluminum proceeds avoiding the ceramic particles.
Through this result a high quality of dissolve resistance is obtained.
(Presented at the 2018 Japan Foundry Engineering Society Conference)
Through this result a high quality of dissolve resistance is obtained.
(Presented at the 2018 Japan Foundry Engineering Society Conference)
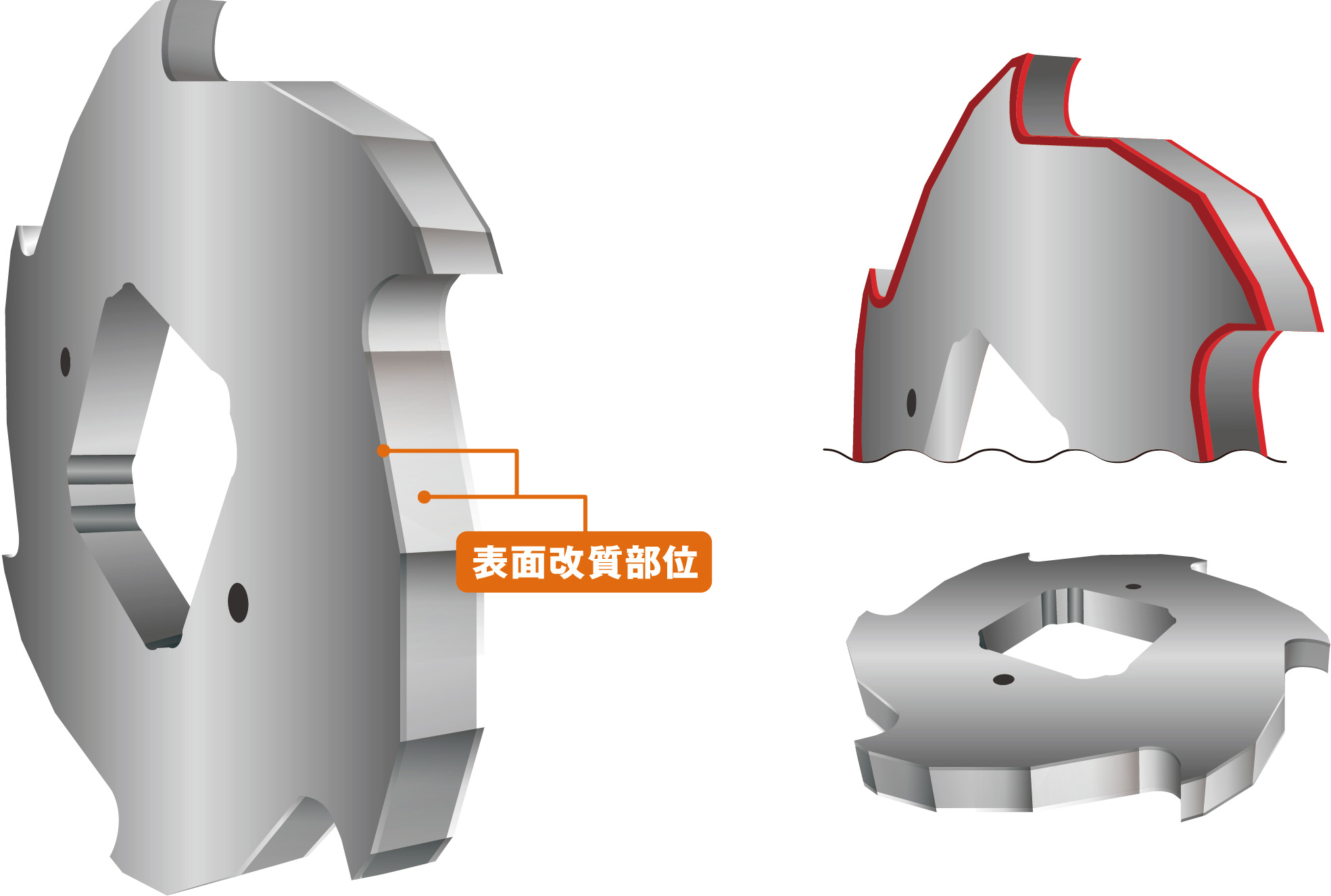
Industrial Knives
Laser Cladded Abrasion Resistant Industrial Knives
Purpose
Exposed to highly abrasive environments, Industrial Knives require high wear resistance and impact resistance.
This Industrial Knife promises high abrasion resistance through Laser Cladding that densely disperses Ceramic Particles, which have higher hardness than metal, into the cutting edge surface.
Additionally, by selecting the most appropriate material for the metal matrix, the product obtains resistance against impact and corrosion under harsh environments.
This Industrial Knife promises high abrasion resistance through Laser Cladding that densely disperses Ceramic Particles, which have higher hardness than metal, into the cutting edge surface.
Additionally, by selecting the most appropriate material for the metal matrix, the product obtains resistance against impact and corrosion under harsh environments.
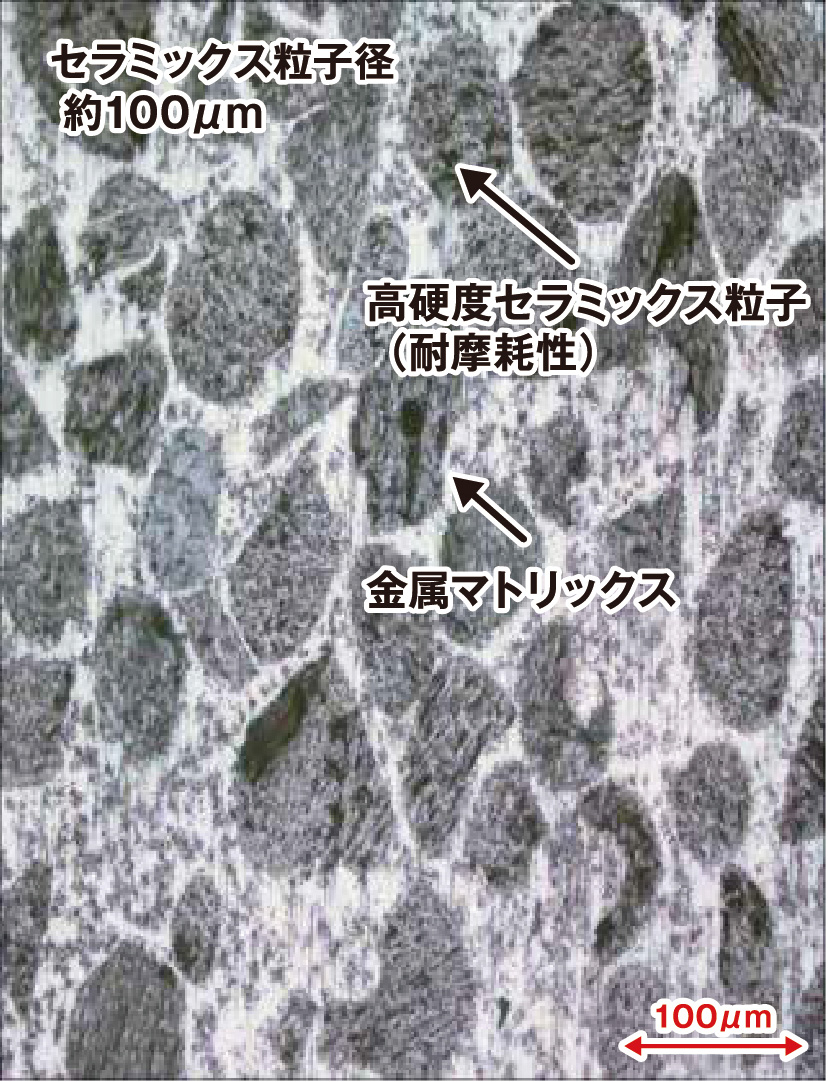
Magnified View of Cladded Layer
| Material | Expected Effects |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Impact Resistance, Corrosion Resistance |
| Nickel Alloy | Impact Resistance, Corrosion Resistance |
| Cobalt Alloy | Abrasion Resistance, Corrosion Resistance |
Cost Reduction due to Laser Quenching

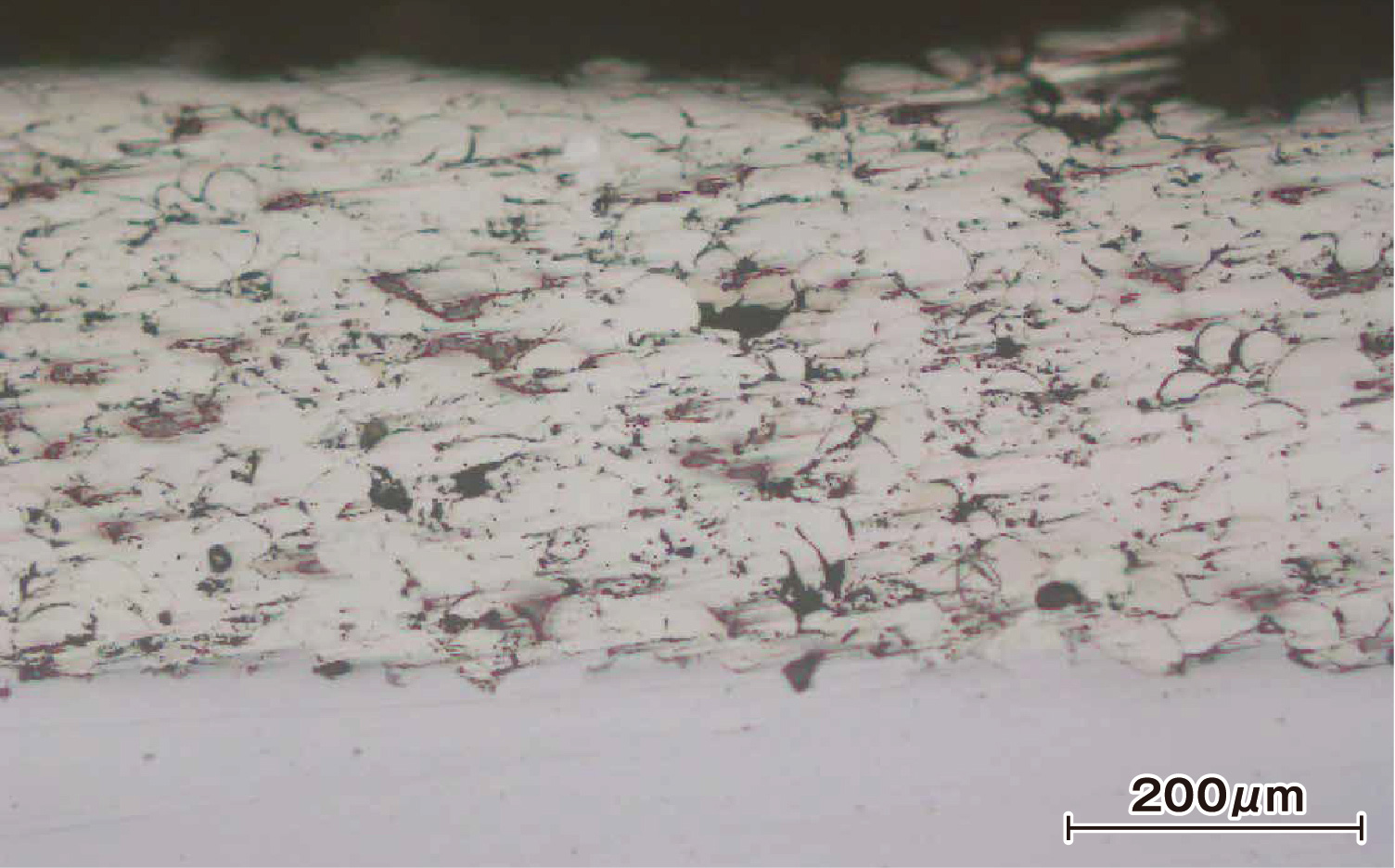
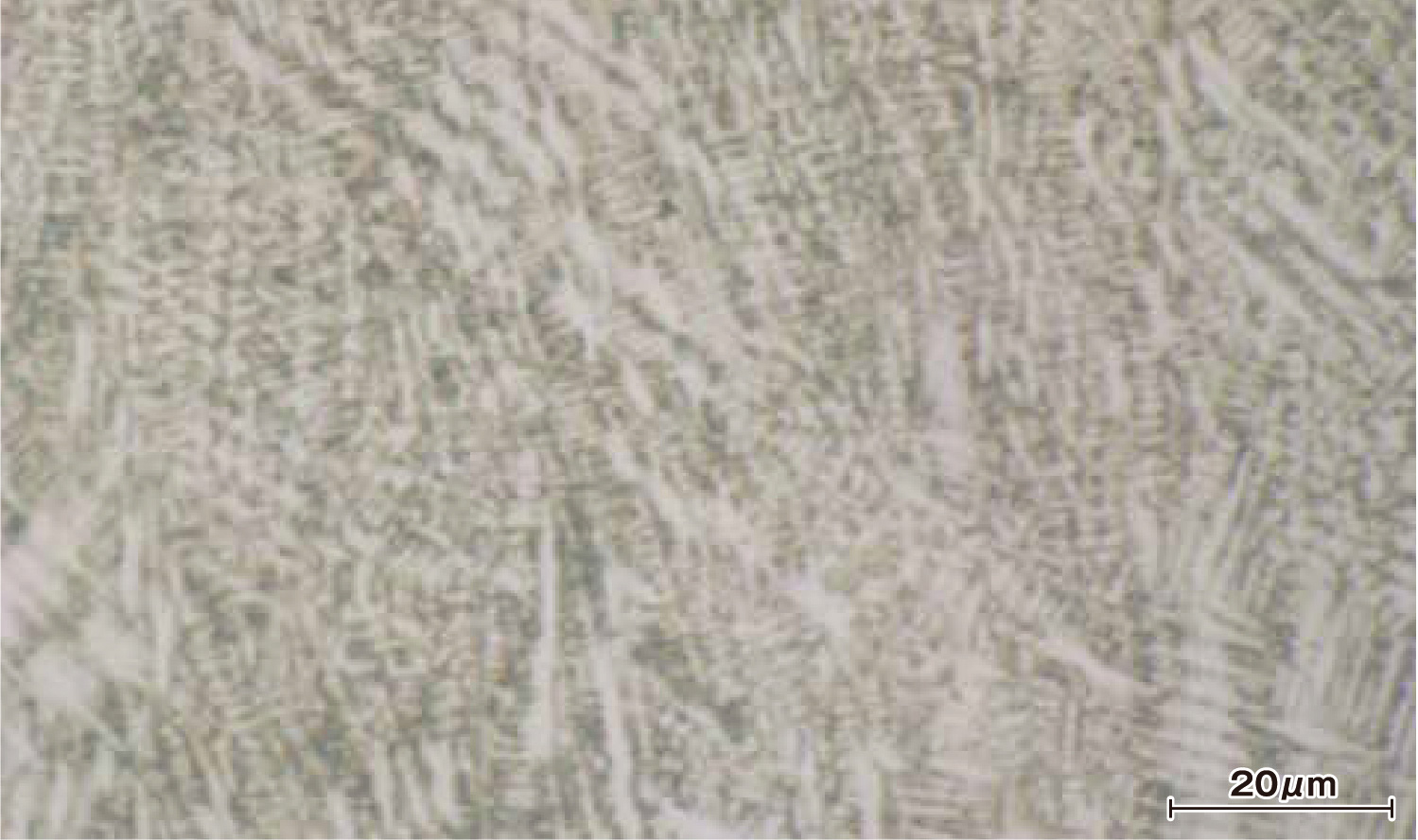
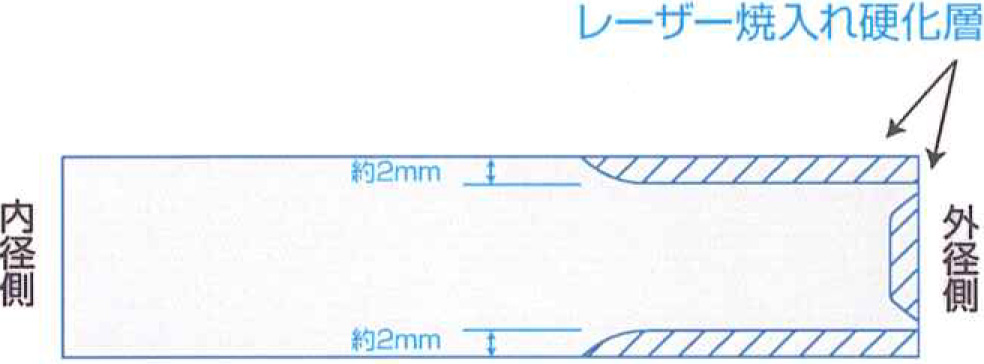
Cross-Sectional Image
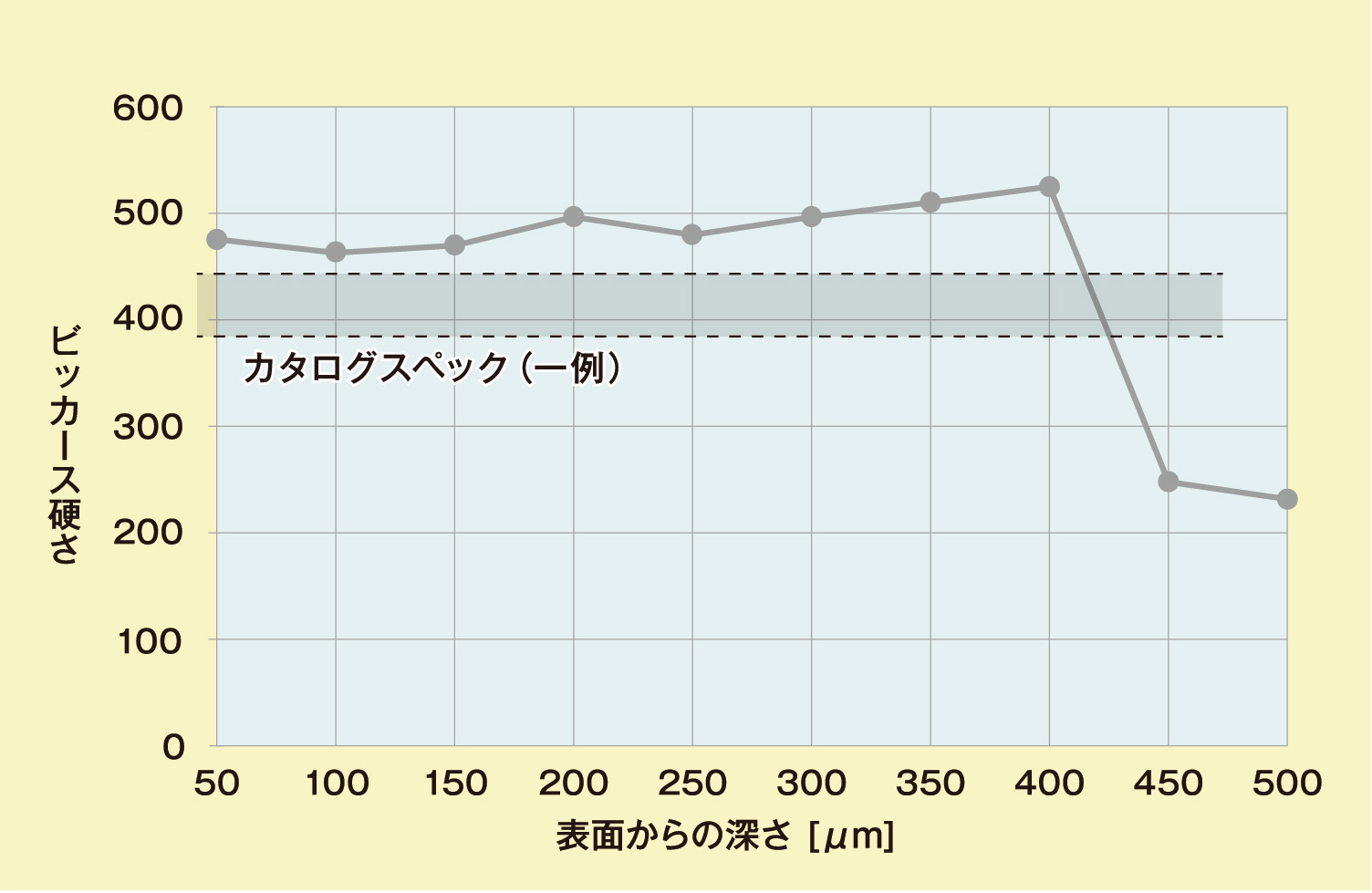
Cross-Sectional Hardness Distribution in the Laser Quenched Area
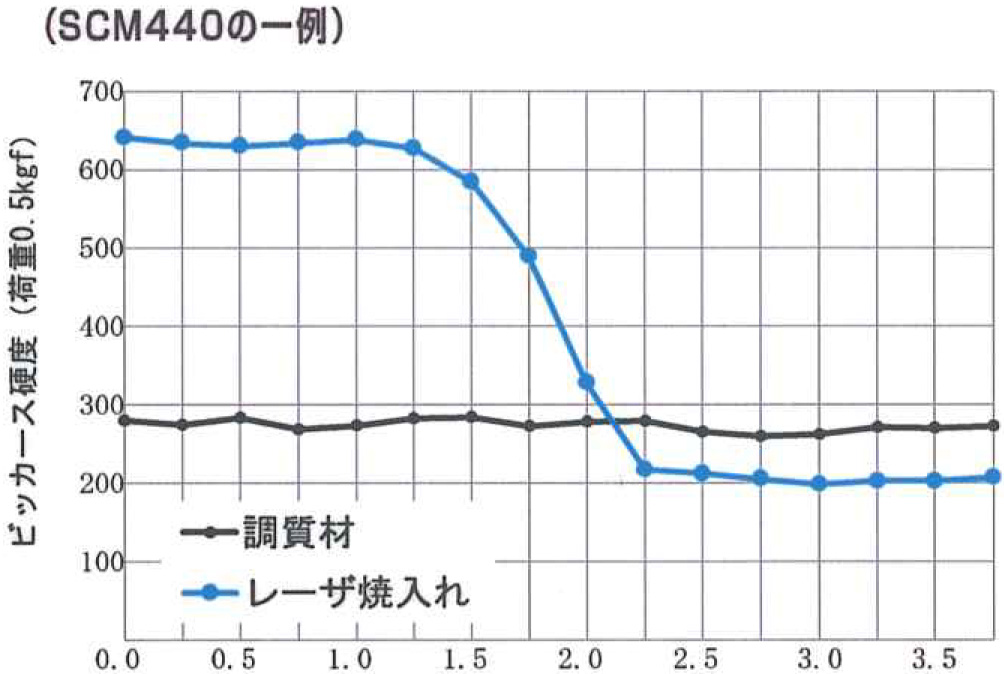
Depth from the Surface (mm)
Characteristics of Laser Quenched Knives
・Achieves cutting edge hardness equivalent to induction hardening, improving wear resistance
・Surface Modification done at a low cost (through measures such as shortened processing time)
・Abrasion resistance and impact resistance is expected through the hybrid knives’ structure of the hardened surface and internal toughness.
Laser Quenched Knives Induces Cost Reduction 2
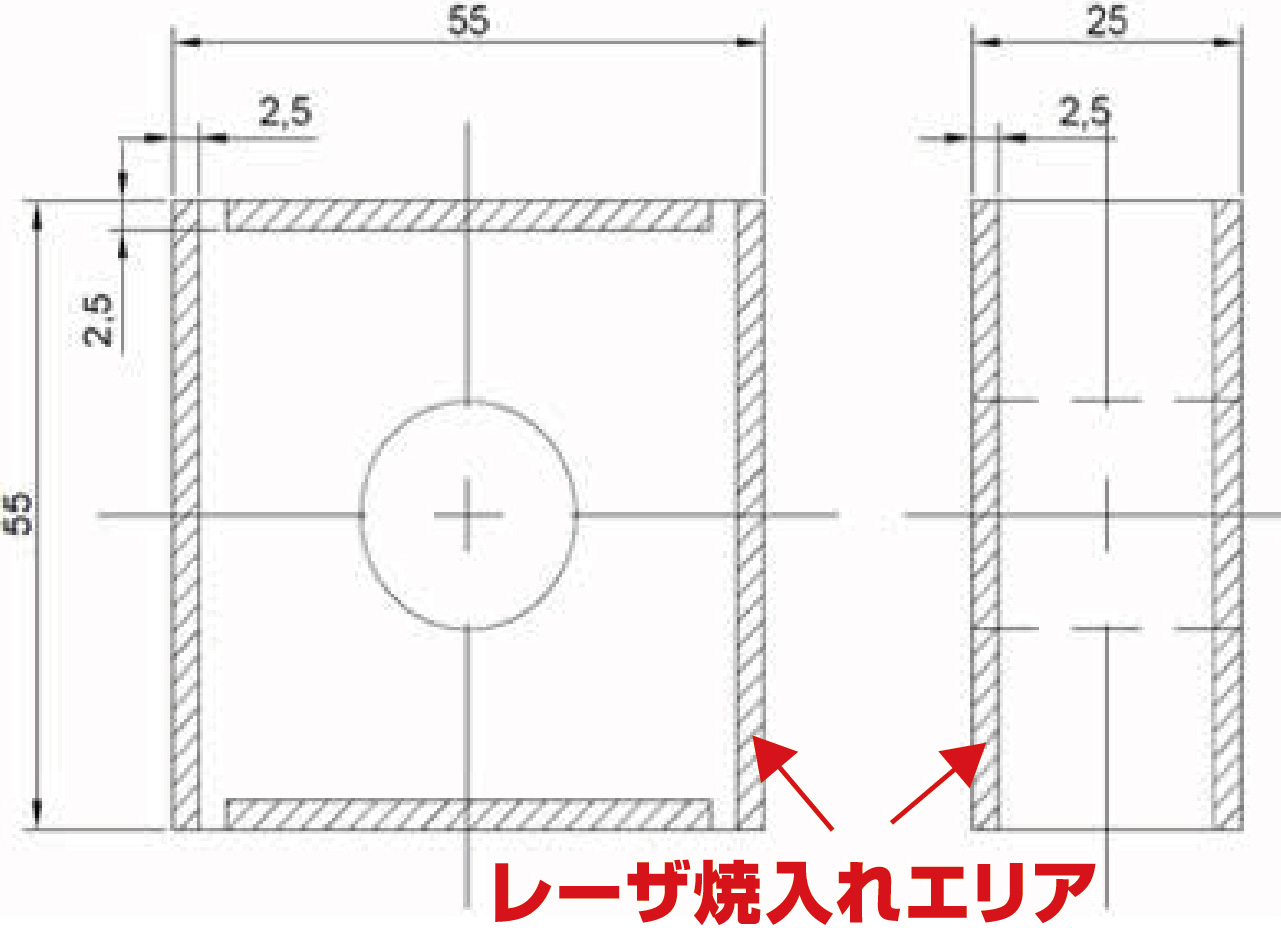
Laser Quenching Processed Area

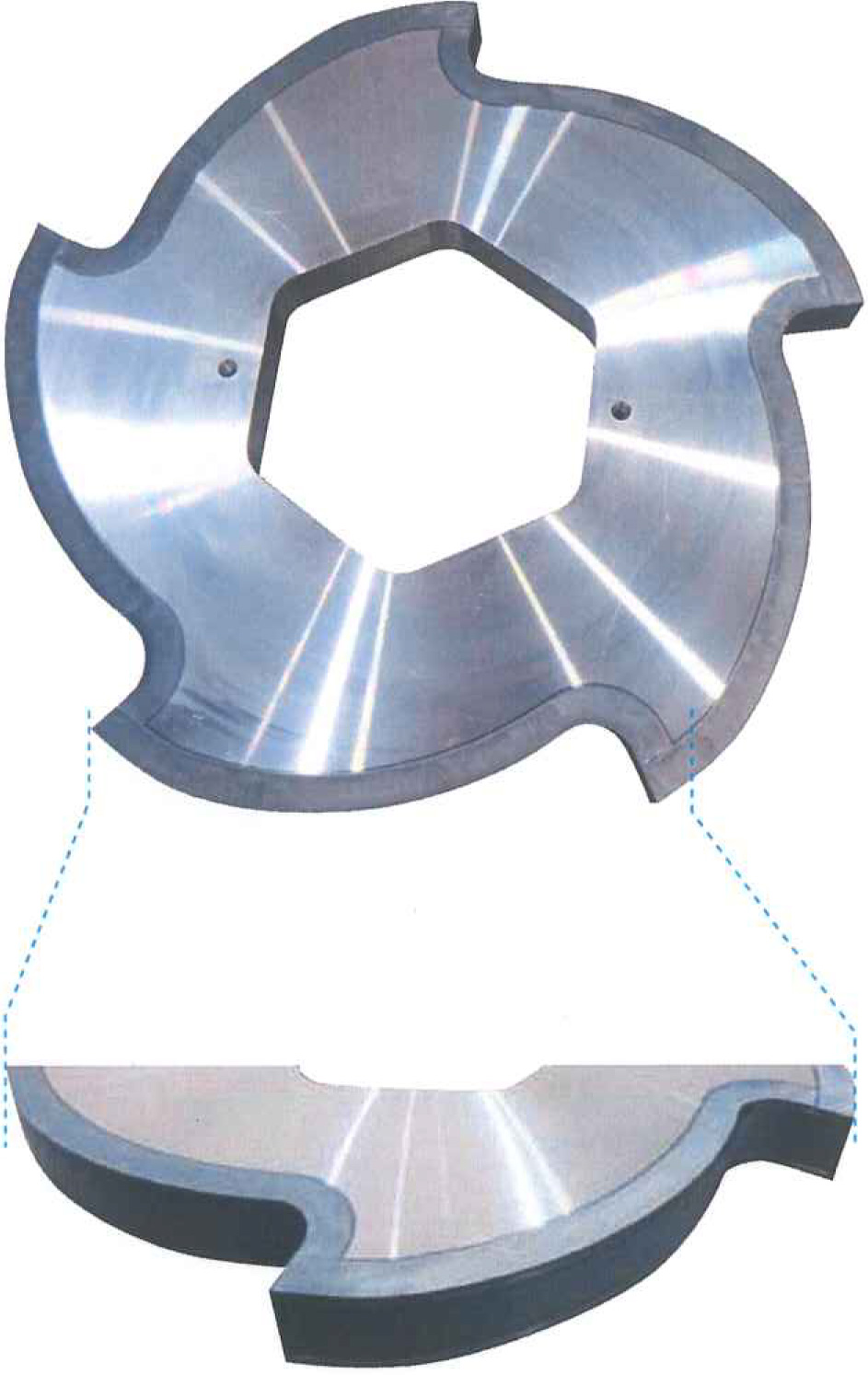
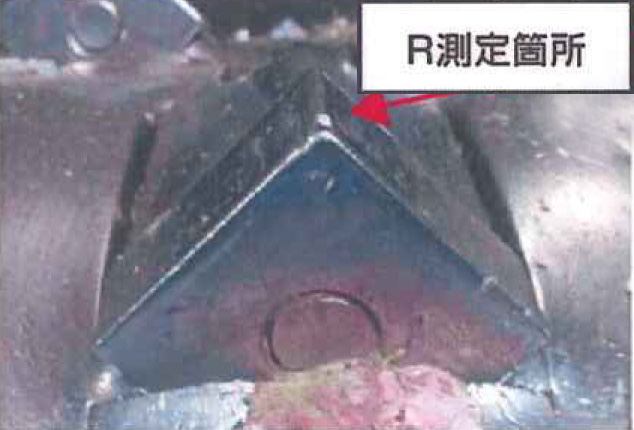
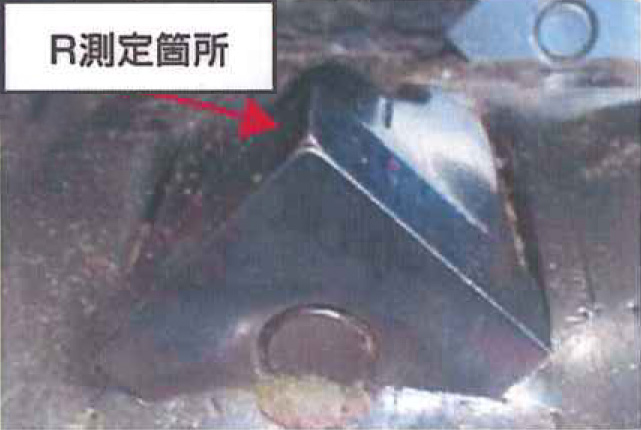
Externa View of Laser Quenched Rotary Blade
| Evaluation Criteria | Laser Quenched Rotary Blade | Dies Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | HRC60~62 (Laser Quenching Hardened Layer Thickness 1.5~2mm) |
HRC56~58 |
| External View after Evaluation |
 |
 |
| Evaluation Time | 215Hr | |
| Amount of Abrasion (Corner) | R2.25 | R2.25 |
Evaluation Results
Features of Laser Quenched Knives
・Holds hardness at par as High-Speed Steel
・
Surface Modification done at a low cost (through measures such as shortened processing time)
・Laser Quenched area is freely adjustable
・Variety of products can be produced in small lots because there are no special equipment
・Abrasion resistance and impact resistance is expected through the hybrid knives’ structure of the hardened surface and internal toughness.
Inspection Equipment that support the development of New Materials and New Technologies
Inspection, Testing equipment

Scanning Electron Microscope

Metallographic microscope
3D Measuring Machine / SONOHARD Hardness Meter / Shore Hardness Measurement Equipment / Micro Vickers Hardness Measurement Equipment / USM35X Krautkramer USM 35X Ultrasonic Inspection Equipment / Metallographic Microscope / Digital Microscope / Analyzing Recorder / Handheld Component Analyzer / Radiation Thermometer / Scanning Electron Microscope / Diode Laser Robotic System / Vacuum Furnace
